Introduction
In the big world of chemistry and atomic science, there exists a fascinating element – Oxygen-28. This super-heavy isotope of oxygen, with its unique properties and characteristics, has attract the attention of scientists and researchers worldwide. In this article, we will understand deep into the world of Oxygen-28, exploring its origins, significance, and applications. Join us on this scientific journey as we unlock the mysteries of this extraordinary element.
Table of Contents
The Basics of Isotopes
Before understanding about Oxygen-28, let’s first get basic understanding of isotopes. Isotopes are variants of an element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. These variations result in different atomic masses while retaining the same chemical properties. Oxygen, a important element for life on Earth, exists in several isotopic forms, with Oxygen -16 being the most abundant and well-known.
Oxygen-28: A Heavy isotope
What Makes It Super-Heavy?
Oxygen-28, often denoted as O-28, stands out due to its remarkable atomic structure. While the most common isotope of oxygen, Oxygen -16, has 8 protons and 8 neutrons, Oxygen-28 have 8 protons and 20 neutrons. This extra neutrons gives Oxygen-28 its super-heavy status, making it significantly heavier than its counterparts.
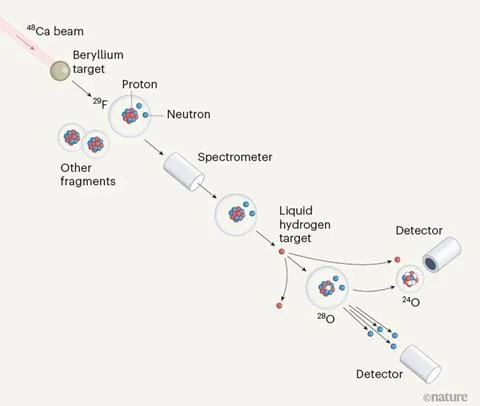
Experimental setup for the creation of oxygen-28
Natural Occurrence
O-28 is not typically found in abundance on Earth. It is considered a rare isotope and is primarily generated through nuclear reactions within high-energy environments, such as nuclear reactors and particle accelerators.
Applications and Significance
Nuclear Physics
One of the key areas where O-28 plays a crucial role is in nuclear physics. Its unique neutron-rich composition makes it an ideal candidate for studying nuclear reactions and the behavior of atomic nuclei. Scientists use O-28 as a tool to gain insights into the fundamental forces governing the universe.
Astrophysical Implications
O-28 existence also has profound implications in astrophysics. It is believed to be involved in the nucleosynthesis processes within massive stars, contributing to the formation of heavier elements through stellar fusion. Understanding Oxygen – 28’s role in these cosmic processes helps to understand the mysteries of our universe’s elemental composition.
Medical Applications
In the field of medicine, researchers are exploring potential applications of O-28 in cancer treatment. Its unique nuclear properties make it suitable for targeted radiation therapy, offering new possibilities for more effective and precise cancer treatments.
The Quest for Oxygen-28
The production and study of O-28 remain a challenged due to its scarcity. Scientists continue to explore innovative methods for creating and isolating this super-heavy isotope. The quest for Oxygen-28 is driven by the desire to expand our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter.
Conclusion
In conclusion, O-28, the super-heavy isotope of oxygen, is a captivating element that holds immense significance in various scientific field. From nuclear physics to astrophysics and potential medical applications, its unique properties continue to inspire researchers worldwide. As we journey deeper into the mysteries of the universe, O-28 stands as a testament to the boundless wonders of the atomic world.
FAQs
1. Is O-28 found naturally on Earth?
No, O-28 is not found in significant quantities on Earth and is primarily created through nuclear reactions in controlled environments.
2. How is O-28 used in nuclear physics?
Oxygen-28’s neutron-rich composition makes it a valuable tool for studying nuclear reactions and atomic nuclei, providing insights into fundamental forces.
3. What role does O-28 play in astrophysics?
O-28 is believed to be involved in the nucleosynthesis processes in massive stars, contributing to the formation of heavier elements in the universe.
4. Are there any practical applications for O-28?
Yes, O-28 is being explored for potential use in cancer treatment, particularly in targeted radiation therapy.
5. Why is O-28 considered a “super-heavy” isotope?
O-28 is deemed super-heavy due to its significantly higher neutron count compared to the more common Oxygen-16, making it substantially heavier.

